The Liberal government tabled much-anticipated legislation Monday that aims to improve water quality in First Nations communities, improve collaboration on water protection and codify a new First Nations-led commission. The long-promised bill, which Indigenous Services Minister Patty Hajdu is touting as the result of immense collaboration and knowledge-sharing, would apply a new framework for source water, drinking water, wastewater and related infrastructure on First Nations land.
Research project aims to safeguard Great Lakes and your drinking water from harmful toxins
Rising global temperatures are causing harmful algal blooms in the Great Lakes which can lead to the emergence of three toxins in the water, according to the past president of the International Ozone Association. Saad Jasim, an adjunct professor at the University of Windsor, is preparing for a new research project to prevent these toxins from entering the drinking water supply.
Calgary says drinking water remains safe following sewage discharge upstream
Calgary officials are monitoring the city’s water supply following a sewer pipe leak in a municipality upstream on the Bow River, but the city says its tap water remains safe to drink. Alberta issued a biological hazard advisory late Saturday, stating a main sewer line break within the Town of Cochrane was causing an overland sewage discharge into the Bow at a bridge along Highway 22.
Why Calgary's drinking water is tasting icky
You may wonder why your water is suddenly tasting mouldy. This unpleasant taste may follow you into the shower, your workplace, gym or college campus. You may have also been losing sleep over thoughts of contaminated water affecting your health. But the reality is nowhere near as dangerous as it seems. City officials say the cause of your worry is geosmin, a “harmless” naturally occurring carbon compound that usually makes its way into Calgary’s reservoirs in late summer or fall.
The 10 Clearest Rivers in Canada
Rivers are the veins of Earth through which nourishment flows—to both the natural and human worlds. They cradle vibrant ecosystems and sculpt our landscapes. They are the living henges we build so much culture, recreation, and commerce around. And their clarity, or lack thereof, points to their health, or lack thereof. And in many ways, our rivers’ health mirrors that of our own. In the expansive lands of Canada, many flow hale and lucid.
Canada and Sask. to invest in drinking water, wastewater infrastructure upgrades
A joint investment of more than $1.7 million dollars to support two green projects in Saskatchewan has been announced. According to a release, Dan Vandal, Minister of Northern Affairs, PrairiesCan and CanNor on behalf of Sean Fraser, Minister of Housing, Infrastructure and Communities and Saskatchewan’s Parks, Culture and Sport Minister Laura Ross new funding will support upgrades to the Danielson Provincial Park sewage lagoon to ensure it complies with regulatory requirements.
Drinking water, aquatic life at risk due to B.C.’s fire-ravaged summer: experts
Experts say the extent to which wildfires have burned across the province this year will have serious implications for the quality of B.C.’s watersheds and the ecosystems that rely on them. John Richardson, a Department of Forest and Conservation Sciences professor at the University of British Columbia, says with so many hillsides scorched by wildfires this year, there’s nothing to prevent incoming rain from creating a “debris torrent” — something which spells bad news for the province’s drinking water.
Montreal mayor says no to water meters as city looks to reduce consumption
As the city of Montreal looks for solutions for its aging, leaky water infrastructure, Mayor Valérie Plante has made it clear that residential water meters are not an option. In theory, meters could be used to charge each household for consumption, thus encouraging people to use less and reduce the strain on a system that is essentially hemorrhaging drinking water.
90% of Great Lakes water samples have unsafe microplastic levels – report
About 90% of water samples taken over the last 10 years from the Great Lakes contain microplastic levels that are unsafe for wildlife, a new peer-reviewed paper from the University of Toronto finds. About 20% of those samples are at the highest level of risk, but the study’s authors say the damage can be reversed if the US and Canada quickly act. “Ninety per cent is a lot,” said Eden Hataley, a University of Toronto researcher and study co-author. “We need to answer some basic questions by monitoring … so we can quantify risks to wildlife and humans.”
Okanagan has one of the highest water use rates per person in Canada
A community consulting firm is asking, ‘Water you doing, Spall?’ The Township of Spallumcheen is looking to get the word out about the critical importance of water conservation. According to Spall reports, the Okanagan has one of the highest rates of water use per person in Canada, meaning there is less water available per person in the Okanagan than anywhere else in the country.
Shoal Lake 40 sues Canada, Winnipeg for years without drinking water, road access
A First Nation, whose lake supplies drinking water to the city of Winnipeg, is suing for a century of alleged damages, according to a statement of claim filed Tuesday. The 13-page “injurious affection claim” seeks unspecified financial damages to compensate for the “devastating impacts of the Winnipeg aqueduct” that isolated the Anishinaabe community for more than 100 years.
Manganese levels remain high in Casselman, Ont. drinking water
Earlier this month, residents raised concerns about drinking water that is dark, appearing dirty or the colour of apple juice. The discoloured water is because of high levels of manganese – a mineral distributed in air, water and soil – present in the South Nation River, according to the municipality. In an update this week, the municipality said it has issued a water quality advisory for the Municipal Water Distribution System due to manganese levels above the Canadian Drinking Water Quality guidelines, and the advisory will remain in effect for further notice.
The governments of Canada and Nova Scotia and the Town and County of Antigonish invest in drinking water infrastructure
This investment will enable the expansion of the St. Joseph's water system, with the addition of a 51,000 gallon (US) storage tank and the construction of approximately 3.6 kilometres of distribution line. This expansion will provide access to drinking water for approximately 40 additional properties, which includes over 650 acres for development. In addition, 2.2 kilometres of distribution line will be added to the Lanark water system. This expansion will provide access to drinking water to approximately 25 properties, including 10 existing residences, a business and over 600 acres for development.
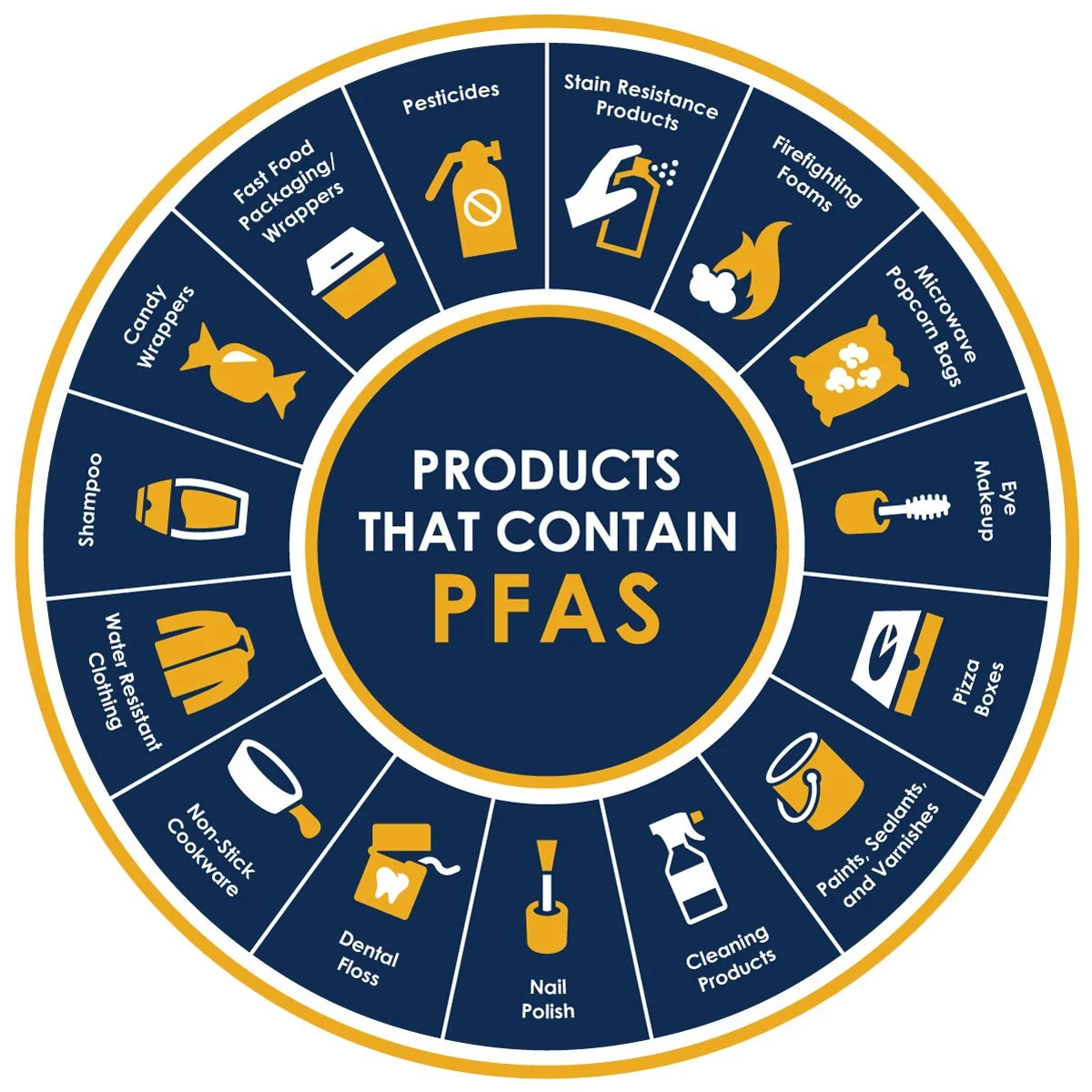
Forever chemicals are in Canadians' air, water and blood - Transcript
MARK RUFFALO: It's basically what they call forever chemicals. They’re long chain fluorocarbons designed to withstand any kind of breakdown. TAMARA KHANDAKER: That's actor and activist Mark Ruffalo talking about PFAS chemicals, also known as forever chemicals. They've been around since the 1940s and used in everything from non-stick pans to takeout containers to cosmetics and fire retardant. But flash forward to today, and the long lasting manmade chemicals have been found inside Canadian blood samples brought in through the air and dust we breathe and even in our drinking water.
Water chemical test kits still available for Newfoundland and Labrador well owners
Private well users in Newfoundland and Labrador are being encouraged to test the quality of their well water for free. The province said over 2,000 well water chemistry kits are still available for pick up through Digital Government and Service N.L. regional offices to provide well owners with detailed information on the chemical levels in their drinking water.
Bathurst hospital faced 3 days without air conditioning after legionella bacteria detected
It confirmed this week that legionella had been detected in three cooling towers at the building, and the air-conditioning system was shut down Wednesday. Tests came back negative after the system was shock-cleaned with chlorine, said a followup note to staff Friday, also obtained by Radio-Canada. The temperatures on the three days when the air conditioning was off ranged from about 27 C to 32 C in Bathurst, according to Environment Canada. Drinking water at the hospital also tested negative, according to the second message to hospital staff.
CANADA: Nunavut's historic land-use plan submitted after 16 years
The federal and Nunavut governments, as well as a group representing Inuit in the territory, are reviewing a massive plan to formally guide where, how and when land and water can be used in Canada's easternmost territory. The plan includes requirements for key wildlife habitat, contaminated sites, military facilities, community areas of interest and drinking water. It aims to balance economic, environmental and social needs.
Asbestos and cement pipes
Following W5’s report, and in an abundance of caution, the City consulted with the Ministry of Environment, Conservation and Parks (MECP) and Wellington-Dufferin-Guelph Public Health. On May 23, 2023, staff collected a sample of water from the Glen Collector System at the Arkell Spring Grounds. Lex Scientific was contracted to analyze the sample and on June 1, 2023, the City received the results of the sample. The Lex Scientific water analysis technical memo indicated tests showed no detection of asbestos fibres in the raw water groundwater sample.
Boil Water Advisory in effect for Janvier
Indigenous Services Canada has issued a Boil Water Advisory to ensure the safety of the community. Copies of these orders can be found at rmwb.ca/water. At around 6:15 a.m. (May 19, 2023) the Janvier water treatment plant temporarily shut down causing a loss of pressure to the water distribution system. At approximately 8:30 a.m., the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo (RMWB) was able to return the plant and distribution pumps to normal.
The world’s largest lakes are shrinking dramatically and scientists say they have figured out why
More than half of the world’s largest lakes and reservoirs have lost significant amounts of water over the last three decades, according to a new study, which pins the blame largely on climate change and excessive water use. Roughly one-quarter of the world’s population lives in the basin of a drying lake, according to the study by a team of international scientists, published Thursday in the journal Science.