The Coxsackie virus was first isolated in Coxsackie, New York in 1948. There are six different Coxsackie B viruses, each responsible for different symptoms and diseases. Coxsackie B viruses are responsible for numerous cases of central nervous system infections in infants and children, as well as heart muscle infections in both children and adults.
Giardia
Detailed Campylobacter
Detailed Cryptosporidium
Detailed Escherichia Coli
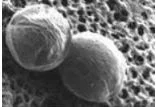
Escherichia coli, also referred to as E. coli, is a type of fecal coliform bacteria that is found in the intestines of healthy warm-blooded animals and humans. Most E. coli strains are harmless and serve a useful function in the body by stopping the growth of harmful bacteria species and by making necessary vitamins. However, some strains can be opportunistic pathogens, while others can cause gastrointestinal illness in healthy humans when ingested.